The binder is one of the basic components of the bonded solid lubricating coating, which largely determines the basic properties of the coating such as adhesion, strength, temperature resistance and curing characteristics, in view of the single component binder resin. It is often difficult to meet the requirements of practical applications. Therefore, the chemical modification of the binder resin by chemical and physical methods is the basis for the development of high performance bonded solid lubricant coatings. In recent years, we have mainly carried out organic/inorganic composite resin modification research; silicone, organotitanium and aromatic heterocyclic polymer modified phenolic, epoxy and novolac epoxy resin; liquid rubber, thermoplastic polymer for thermosetting Research on toughening modification of coating resin. The purpose is to improve the high temperature resistance, medium resistance and comprehensive physical and mechanical properties of the original resin while maintaining the bonding properties of the original resin. It has been found that the terminal hydroxyl groups in silicone and organotitanium can undergo condensation reaction with hydroxymethyl and epoxy groups in phenolic and epoxy resins, respectively, and the chain bonds between the two to form silicone. The three-phase network structure of the chain can improve the temperature resistance by a large degree of radiation while maintaining the bonding strength of the original resin; the thermoplastic aromatic heterocyclic polymer and the liquid nitrile rubber can be combined with most of the thermosetting resins. The realization of molecular level recombination and the formation of polymer alloys have significantly improved the toughness and comprehensive physical and mechanical properties of the composite resin. The above research results have made it possible to prepare organic high temperature resistant, high load resistant, long life bonded solid lubricating coatings. 3.2 Study on the lubrication and failure mechanism of bonded solid lubricating coatings The lubrication process of bonded solid lubricating coatings was analyzed by the frictional adhesion theory. The expression of friction coefficient under the condition of coating lubrication was obtained: Previous Next Steel Grating / Checkered Plate Steel Grating,Checkered Plate,Galvanized Grating Steel Anping Tianshun Metal Net Co., Ltd. , http://www.chawiremesh.com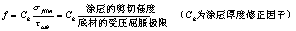
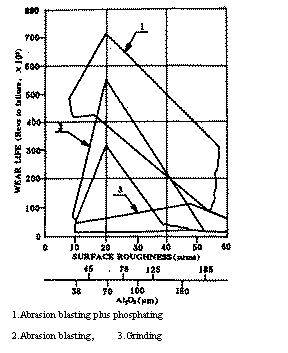
This formula is very similar in form to the general theoretical lubrication theory of the film. The difference is that a film thickness correction factor is given, which gives the essence of the lubrication of the bonded solid lubricating coating and improves the tribological properties of the coating. The ability, lubrication performance); systematically studied the impact of friction conditions on the tribological properties of various bonded solid lubricant coatings, found that coatings with layered solids such as MoS2, graphite as lubricants, sliding The speed ratio load has a greater influence on the wear life of the coating, that is, the service life of the coating under heavy load and low speed is longer than the wear life under the low load and high speed under the same PV value, which is suitable for solving Tribological problems in low- and high-load conditions, while for PTFE-based coatings, the tribological properties are greatly affected by the load, and the lower friction coefficient and longer under medium and low load conditions. Wear life; the physical and mechanical properties of the bonded solid lubricating coating and the influence of the modified filler on its tribological properties were studied. It was found that the flexibility of the coating and the hard filler affect its load carrying capacity. An important factor, nano-filler can significantly improve the formation of transfer film during the friction process and greatly extend its wear life, thus guiding the development of a variety of bonded solid lubricant coating materials with ultra-high load carrying capacity. The ultimate bearing capacity is several times higher than that of conventional lubricating materials. The wear failure process of bonded solid lubricating coatings was investigated. It was found that the formation, expansion and formation of frictional surface bubbles (Fig. 6) during the frictional process of bonded solid lubricating coatings The rupture is the main reason for its accelerated failure, and it is proposed that the formation of bubbles is mainly due to the plastic deformation of the coating due to friction, which causes the friction surface of the coating to partially relax. Further friction causes bubbles to form and gradually grow in the relaxed membrane. The view that the coating is worn out due to cracking, which proves that the coating wear fails, confirms that the interface between the coating and the substrate improves the thermal conductivity of the friction surface, and can effectively suppress the generation and expansion of bubbles during the rubbing process. Extend the wear life of the coating. The above research results have theoretical guiding significance for us to understand the lubricating nature of bonded solid lubricating coatings, determine the optimum coating thickness and the role of friction transfer film, and develop low friction, high load bearing and long life bonded solid lubricating coatings.