1 base point coordinate calculation 1) Base point: The intersection or tangent point of the different geometric lines that make up the contour of the part is called the base point. For example, the intersection of a straight line and a straight line, the intersection or tangent point of a straight line and an arc, the intersection or tangent point of an arc and a quadratic curve, and the like. 2) Calculation example: Figure 2.12 Base point A, B, D, E coordinate values ​​can be directly found, not shown in the C point chart, and the simultaneous equations are solved. 2 node coordinate calculation When the shape of the part is composed of curves other than straight lines or arc segments (such as involute, hyperbola, list curve, etc.), and the numerical control system does not have the interpolation function of these curves, the numerical calculation is more complicated. At this time, the approximation method can be used for processing. 1) Node: Use a number of straight or circular segments to approximate a given curve. The intersection or tangent point of a straight line or arc segment is called a node. 2) Coordinate calculation: the number of nodes is determined by the shape of the processed curve, the shape of the approaching line segment and the allowable interpolation error; generally, the computer solves and calculates the coordinate values ​​of all nodes; when the numerical control system has the corresponding geometric curve When interpolating, you only need to find the coordinates of the base point. Acrylic Neon Sign,Acrylic Neon Light,Acrylic Box Neon Sign,Neon Acrylic Light Guangdong Yuansheng Ad.&Lightings Co,Ltd. , https://www.pilottsignonline.com
According to the processed part pattern, according to the determined machining route and the allowable programming error, the data required for the numerical control system is calculated, which is called numerical calculation. 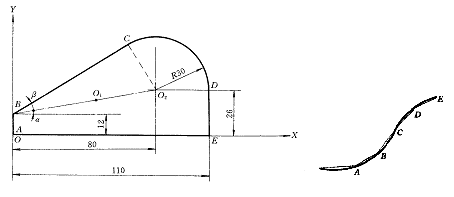
Figure 1 Base point of the part outline Figure 2 Node 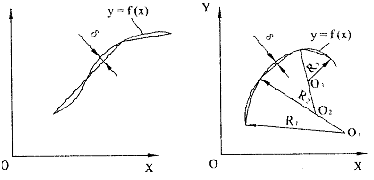
Figure 3 Approximation of the curve