Brass is a special copper alloy. Brass is an object made of an alloy of copper and zinc. It gets its name from its yellow color. Brass with 56% to 68% copper has a melting point of 934 to 967 degrees. Brass has good mechanical properties and wear resistance. Because of its unique advantages, it has become an important part of the parts manufacturing industry. It is generally used for precision copper parts such as automobile parts, medical parts and electrical parts. Brass Precsion Turned Parts,Brass Precision Parts,Brass Turned Components,Brass Precision Turned Parts Stand Dragon Industrial Co., Ltd. , https://www.standdragontw.com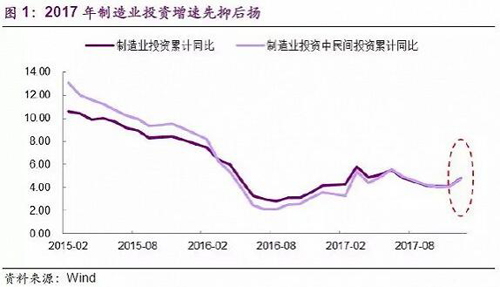 To answer these questions, data analysis is not enough, because supply-side reforms pose a huge challenge to traditional analytical perspectives. From a traditional perspective, the analysis of the short-term economic evolution mainly depends on changes in demand, but the supply-side reform has greatly reduced the traditional demand analysis. For example, a small number of unstated small and micro enterprises were shut down due to environmental issues, which led to the transfer of orders to large enterprises, which led some large enterprises to expand production capacity. Behind this is not the need for improvement but the contraction of supply. So how do you view these new phenomena? Looking at the data may be misleading, and field research is very important. To this end, the macro group of Everbright Securities conducted field research in an industrial park in a certain city in the east in early February 2018. The private manufacturing industry in the province where the city is located is very developed. Our research covers a wide range of industries, including high-tech and government-backed industries, as well as traditional manufacturing. These industries include the pharmaceutical industry (both Chinese and Western medicine), automobile and motorcycle manufacturing, valve manufacturing, machinery manufacturing, leather processing and manufacturing, chemical industry, and electrical appliance manufacturing. In addition, in order to have a more comprehensive understanding of the situation in the manufacturing industry, we also conducted interviews with local government agencies and state-owned banks. The city is located in the Yangtze River Delta region. In 2017, GDP accounted for nearly 3% of the province's total, the secondary industry accounted for 43%, and the tertiary industry accounted for 49%, mainly in manufacturing and tourism. The industrial park we surveyed is a national-level development zone. In 2017, the industrial output value reached nearly 20 billion, a year-on-year increase of 17%. There are hundreds of manufacturing enterprises in the region, mainly in the fields of synthetic leather, plastic products, machinery manufacturing, auto parts, bio-pharmaceuticals, etc. It is a national-level intelligent equipment and robot industry base, integrating traditional industries and high-tech industries. Strong representation in manufacturing (mainly small and medium-sized enterprises). As early as July 2016, our research team conducted research on dozens of manufacturing industries in the region and released a research report. How far is the spring of manufacturing? 》. The situation at the time was that basically all the manufacturing days were not so good, the problem of overcapacity was serious, and the tide of closure was not over. Although the local government actively improved the environment for the manufacturing industry, the spring of manufacturing was still far away. As we stated in the 2018 Annual Outlook Report, “Being a War of Inflection, Buying “Fairnessâ€â€, the pursuit of efficiency before the 19th National Congress and the pursuit of “fairness†after the 19th National Congress. The pursuit of "fairness" in the manufacturing year of the beginning of the year? We have about one and a half years from the last time of this survey. What is the situation? Has the spring of manufacturing been coming? Has the demand improved? Our research shows that the overall demand for manufacturing has not improved significantly, the industry is quite different, and the demand for emerging industries, high-tech industries, and government-backed industries is better. For example, a company that we visited as an air-energy water heater benefited from “coal to electricityâ€. In 2015, the net profit was only over 10 million yuan. In 2016, the net profit was more than 30 million yuan, and the net profit in 2017 reached 6,000. More than 10,000 yuan. Sales are also gradually increasing. In 2015, it was close to 200 million yuan, 300 million yuan in 2016, and nearly 600 million yuan in 2017. The visiting Chinese medicine industry reflects that its development is strongly supported by the government, and the increase in income has led to an increase in people's attention to health, and the growth of industry demand is relatively stable. However, the demand for traditional manufacturing industry has not improved. Due to environmental protection and safety supervision policies, “low-small†enterprises have gradually closed down or been merged by large enterprises. According to the website of the municipal government, the city’s elimination of backward production capacity in 2017 involves 78 enterprises. The low-small enterprises have nearly 700 rectifications, and the survival of the fittest is obvious. The industry concentration of traditional manufacturing is gradually increasing. â— The artificial leather, automobile and motorcycle parts, chemical products and other enterprises we visited generally reflect that the overall market demand has not improved significantly. For example, the automobile and motorcycle companies have indicated that the overall market demand growth has remained at 5-6% since 2016, and will continue to maintain this trend in the future. . The demand for automotive lighting industry is stable and the competition is fierce. The profit margin depends on the OEMs and models, and the profit margin has declined in the past few years. Due to the price cuts of the main car manufacturers, the auto parts companies also need to cut prices due to the impact of industry linkages. The auto industry has overcapacity and price wars are prevalent. The large-scale artificial leather enterprises we visited reflected that the capacity utilization rate has not returned to normal, the orders have not increased significantly, and the capacity utilization rate has not increased much. The motor and industrial sewing machine manufacturers visited also said that the industry is in a state of saturation. â— However, environmental protection and safety supervision policies have led to the gradual closure of “low-small†enterprises or mergers and acquisitions by large enterprises. Some orders have shifted from small and micro enterprises to large and medium-sized enterprises, which has increased the concentration of the industry. This process is still not over. For example, the chemical companies we visited believe that one-third of the enterprises in the industry have closed down, one-third of the enterprises are still in a difficult situation, and the remaining one-third can continue to develop; the leather companies that have visited in recent years have acquired three companies that have closed down. The pharmaceutical companies reflected that they were affected by the environmental protection policy, and the upstream raw material drug companies had a bankruptcy tide; the valve companies began to show a collapse in 2015, which is not yet over. After the “low-small†enterprises closed down, the orders gradually shifted to large enterprises, and the concentration of the industry continued to increase. Some of the respondents indicated that 20% of the increase in demand was caused by this reason. From a national perspective, Figure 2-3 also shows a similar situation.
To answer these questions, data analysis is not enough, because supply-side reforms pose a huge challenge to traditional analytical perspectives. From a traditional perspective, the analysis of the short-term economic evolution mainly depends on changes in demand, but the supply-side reform has greatly reduced the traditional demand analysis. For example, a small number of unstated small and micro enterprises were shut down due to environmental issues, which led to the transfer of orders to large enterprises, which led some large enterprises to expand production capacity. Behind this is not the need for improvement but the contraction of supply. So how do you view these new phenomena? Looking at the data may be misleading, and field research is very important. To this end, the macro group of Everbright Securities conducted field research in an industrial park in a certain city in the east in early February 2018. The private manufacturing industry in the province where the city is located is very developed. Our research covers a wide range of industries, including high-tech and government-backed industries, as well as traditional manufacturing. These industries include the pharmaceutical industry (both Chinese and Western medicine), automobile and motorcycle manufacturing, valve manufacturing, machinery manufacturing, leather processing and manufacturing, chemical industry, and electrical appliance manufacturing. In addition, in order to have a more comprehensive understanding of the situation in the manufacturing industry, we also conducted interviews with local government agencies and state-owned banks. The city is located in the Yangtze River Delta region. In 2017, GDP accounted for nearly 3% of the province's total, the secondary industry accounted for 43%, and the tertiary industry accounted for 49%, mainly in manufacturing and tourism. The industrial park we surveyed is a national-level development zone. In 2017, the industrial output value reached nearly 20 billion, a year-on-year increase of 17%. There are hundreds of manufacturing enterprises in the region, mainly in the fields of synthetic leather, plastic products, machinery manufacturing, auto parts, bio-pharmaceuticals, etc. It is a national-level intelligent equipment and robot industry base, integrating traditional industries and high-tech industries. Strong representation in manufacturing (mainly small and medium-sized enterprises). As early as July 2016, our research team conducted research on dozens of manufacturing industries in the region and released a research report. How far is the spring of manufacturing? 》. The situation at the time was that basically all the manufacturing days were not so good, the problem of overcapacity was serious, and the tide of closure was not over. Although the local government actively improved the environment for the manufacturing industry, the spring of manufacturing was still far away. As we stated in the 2018 Annual Outlook Report, “Being a War of Inflection, Buying “Fairnessâ€â€, the pursuit of efficiency before the 19th National Congress and the pursuit of “fairness†after the 19th National Congress. The pursuit of "fairness" in the manufacturing year of the beginning of the year? We have about one and a half years from the last time of this survey. What is the situation? Has the spring of manufacturing been coming? Has the demand improved? Our research shows that the overall demand for manufacturing has not improved significantly, the industry is quite different, and the demand for emerging industries, high-tech industries, and government-backed industries is better. For example, a company that we visited as an air-energy water heater benefited from “coal to electricityâ€. In 2015, the net profit was only over 10 million yuan. In 2016, the net profit was more than 30 million yuan, and the net profit in 2017 reached 6,000. More than 10,000 yuan. Sales are also gradually increasing. In 2015, it was close to 200 million yuan, 300 million yuan in 2016, and nearly 600 million yuan in 2017. The visiting Chinese medicine industry reflects that its development is strongly supported by the government, and the increase in income has led to an increase in people's attention to health, and the growth of industry demand is relatively stable. However, the demand for traditional manufacturing industry has not improved. Due to environmental protection and safety supervision policies, “low-small†enterprises have gradually closed down or been merged by large enterprises. According to the website of the municipal government, the city’s elimination of backward production capacity in 2017 involves 78 enterprises. The low-small enterprises have nearly 700 rectifications, and the survival of the fittest is obvious. The industry concentration of traditional manufacturing is gradually increasing. â— The artificial leather, automobile and motorcycle parts, chemical products and other enterprises we visited generally reflect that the overall market demand has not improved significantly. For example, the automobile and motorcycle companies have indicated that the overall market demand growth has remained at 5-6% since 2016, and will continue to maintain this trend in the future. . The demand for automotive lighting industry is stable and the competition is fierce. The profit margin depends on the OEMs and models, and the profit margin has declined in the past few years. Due to the price cuts of the main car manufacturers, the auto parts companies also need to cut prices due to the impact of industry linkages. The auto industry has overcapacity and price wars are prevalent. The large-scale artificial leather enterprises we visited reflected that the capacity utilization rate has not returned to normal, the orders have not increased significantly, and the capacity utilization rate has not increased much. The motor and industrial sewing machine manufacturers visited also said that the industry is in a state of saturation. â— However, environmental protection and safety supervision policies have led to the gradual closure of “low-small†enterprises or mergers and acquisitions by large enterprises. Some orders have shifted from small and micro enterprises to large and medium-sized enterprises, which has increased the concentration of the industry. This process is still not over. For example, the chemical companies we visited believe that one-third of the enterprises in the industry have closed down, one-third of the enterprises are still in a difficult situation, and the remaining one-third can continue to develop; the leather companies that have visited in recent years have acquired three companies that have closed down. The pharmaceutical companies reflected that they were affected by the environmental protection policy, and the upstream raw material drug companies had a bankruptcy tide; the valve companies began to show a collapse in 2015, which is not yet over. After the “low-small†enterprises closed down, the orders gradually shifted to large enterprises, and the concentration of the industry continued to increase. Some of the respondents indicated that 20% of the increase in demand was caused by this reason. From a national perspective, Figure 2-3 also shows a similar situation. 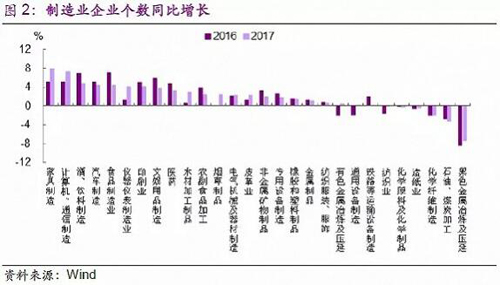
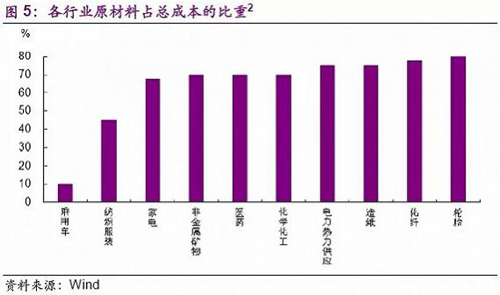
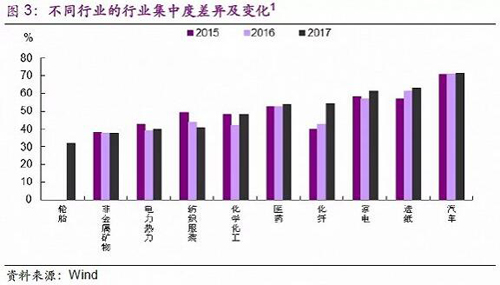 Second, the demand for enterprises in some traditional industries has improved, but this is mainly because the cakes have grown spontaneously, but each has its own special reasons. For example, the valve company that was visited indicated that demand is improving. In 2017, it undertook a large order because a hydropower station was built in the northwest region (infrastructure promotion). At the same time, rising oil prices have also driven demand for valves, as customers change their valves every two years when the price of oil is below $60/barrel, and every year when they are above $60/bbl. Third, the export of manufacturing has improved, but the improvement of external demand is not the only reason for the improvement of exports, but also the improvement of the company's own marketing. For example, 70% of a valve enterprise product we surveyed is used for export, and its export increase is due to the improvement of external demand, but the more important one is limited domestic demand and increased overseas marketing and expansion. In other words, it is because the company's own product quality and marketing are improving (for its own reasons), rather than the export demand of the entire industry is improving. At present, the impact of the appreciation of the renminbi on external demand has not yet been reflected, but it will be reflected in the future. For example, when we visit an export chemical company to sign the annual order, the price does not move after the signing. In order to ensure the profit, the raw materials also do so, so it is equivalent to locking the profit, but there may be some impact in the future. Raw materials and environmental costs rise, affecting geometry? The supply-side reforms started in 2015 have led to rising prices of raw materials such as coal and steel, but the price hikes on the downstream manufacturing industry do not seem to be very obvious. It seems that “the winners are less losers†(Figure 4), major industries The proportion of raw materials to cost is shown in Figure 5. . In our special report, "The cost is soaring, can the winners and losers continue to lose? In the detailed analysis, this survey also has a field understanding. The rising cost of raw materials and the increase in environmental protection costs have squashed the traditional manufacturing profits. The large-scale, top-income artificial leather company we visited said that although the current income and sales volume is increasing, the profit is declining and basically in a state of capital preservation. The main reason lies in two points: First, the overall market demand has not improved significantly. The technological innovation of traditional industries is limited. The increase in raw material price and sales price cannot increase in the same proportion, which squashes corporate profits. Second, environmental protection has also increased the cost of corporate squeeze. The cost of environmental protection has increased year by year. The environmental protection expenditure of the company's new cost is about half. The environmental protection cost will not produce direct benefits, but only improve the external environment. At present, wastewater and waste gas are monitored online, even rainwater, from culvert monitoring to surface monitoring, and the standard is improved.
Second, the demand for enterprises in some traditional industries has improved, but this is mainly because the cakes have grown spontaneously, but each has its own special reasons. For example, the valve company that was visited indicated that demand is improving. In 2017, it undertook a large order because a hydropower station was built in the northwest region (infrastructure promotion). At the same time, rising oil prices have also driven demand for valves, as customers change their valves every two years when the price of oil is below $60/barrel, and every year when they are above $60/bbl. Third, the export of manufacturing has improved, but the improvement of external demand is not the only reason for the improvement of exports, but also the improvement of the company's own marketing. For example, 70% of a valve enterprise product we surveyed is used for export, and its export increase is due to the improvement of external demand, but the more important one is limited domestic demand and increased overseas marketing and expansion. In other words, it is because the company's own product quality and marketing are improving (for its own reasons), rather than the export demand of the entire industry is improving. At present, the impact of the appreciation of the renminbi on external demand has not yet been reflected, but it will be reflected in the future. For example, when we visit an export chemical company to sign the annual order, the price does not move after the signing. In order to ensure the profit, the raw materials also do so, so it is equivalent to locking the profit, but there may be some impact in the future. Raw materials and environmental costs rise, affecting geometry? The supply-side reforms started in 2015 have led to rising prices of raw materials such as coal and steel, but the price hikes on the downstream manufacturing industry do not seem to be very obvious. It seems that “the winners are less losers†(Figure 4), major industries The proportion of raw materials to cost is shown in Figure 5. . In our special report, "The cost is soaring, can the winners and losers continue to lose? In the detailed analysis, this survey also has a field understanding. The rising cost of raw materials and the increase in environmental protection costs have squashed the traditional manufacturing profits. The large-scale, top-income artificial leather company we visited said that although the current income and sales volume is increasing, the profit is declining and basically in a state of capital preservation. The main reason lies in two points: First, the overall market demand has not improved significantly. The technological innovation of traditional industries is limited. The increase in raw material price and sales price cannot increase in the same proportion, which squashes corporate profits. Second, environmental protection has also increased the cost of corporate squeeze. The cost of environmental protection has increased year by year. The environmental protection expenditure of the company's new cost is about half. The environmental protection cost will not produce direct benefits, but only improve the external environment. At present, wastewater and waste gas are monitored online, even rainwater, from culvert monitoring to surface monitoring, and the standard is improved. 
 But not all industries are plagued by cost increases, such as companies that are expanding upstream are less squeezed. The air-energy water heater companies we visited reflected that although the cost of raw materials accounted for a relatively high proportion, the company itself set up an accessory shop, and many of the parts were produced by themselves to hedge against the squeeze of profits. The good companies left in the tide of bankruptcy have stronger bargaining power and are less squeezed in the process of raw material price hikes. For example, a chemical company we visited survived after the large-scale bankruptcy caused by environmental safety supervision. Although the price of raw materials rose, the demand was stable, the demand exceeded supply, the bargaining power increased, and the prices of raw materials increased while the prices of raw materials rose. The squeeze on profits is small. There are also those companies whose pricing model is cost-plus, and the price increase of raw materials has little impact on corporate profits. For example, we are visiting a cost-added socket manufacturing enterprise with a strict budget and financial system. In advance, we will increase the price of the product according to the price of raw materials and transfer the price increase to the downstream. Auto parts companies said that raw material prices have risen, mainly by tapping and improving their ability to reduce costs and increase efficiency. The fastest-growing raw materials include plastic resins for luminaires; this squeezes profits but can reduce other costs to ease and partially pass downstream. In general, the increase in raw material prices and the increase in environmental protection costs have increased the profits of traditional manufacturing industries. However, the enterprises that have expanded upstream, the industries with bargaining power, and the cost-added industries have relatively little impact on profits. Has the financing situation improved? The regulatory storm caused the financing conditions of the whole society to tighten, the effective loan interest rate remained high, and the bond market income did not see a downward trend, while the social financing and broad money growth rates both fell sharply. So, what are the financing conditions for manufacturing? From the perspective of our research, the current bank risk appetite is still low, and the choice of lending industry is quite different. The loans are mainly invested in infrastructure, personal consumer loans and housing mortgage loans, and the development loans have not been loosened. As far as manufacturing is concerned, banks are mainly investing in emerging industries, high-tech industries and leading enterprises. The financing of traditional manufacturing and small and medium-sized enterprises is still difficult. Among the companies visited, there are two new three-board companies, one listed company, a subsidiary of a listed company (the parent company is responsible for the allocation of funds, and they will not finance at all), and the rest of the companies are financed by banks. Among the large state-owned banks interviewed, the basic situation of loan investment is as follows: â— Bank A indicates that the infrastructure accounted for 30-40% of the loans, 10% of the small and medium-sized enterprises, and the rest are personal loans. â— Bank-related loans in Bank B account for 20%, and the manufacturing industry basically does not invest in traditional industries. The main reason is that the bank previously released a large amount of loans through mortgages, joint guarantees, etc., resulting in large-scale bad, and the new lending policy is strictly Tight, does not involve traditional manufacturing, but has strong support for education, medical care, pension, tourism and other industries. â— C Bank is a supporter of township and village enterprises. It has more manufacturing loans. It is similar to Bank B. It originally invested more traditional industries, but it was later in the development zone, and the losses were less than those of Bank B. The traditional industry only supplements the working capital, does not give expansion funds, and mainly supports the development of tourism, culture, new materials, new energy, information technology and other industries. â— D-bank infrastructure loans account for 60%, personal mortgages account for 10%, and the remaining 30% are in manufacturing. Enterprises in the manufacturing industry do not enter the traditional industry, and enterprises that do not meet the environmental standards do not issue loans. The financing problems faced by the responding manufacturing enterprises are mainly reflected in the following aspects: â— The current bank loanable funds are abundant, but the overall risk appetite is still low. One important reason is that the impact of mutual insurance mutual protection still exists, and the bank The outlook for traditional manufacturing is not very optimistic, while emerging industries and leading companies have limited financing needs. Among the companies visited, the corporate debt pressure caused by joint guarantee and mutual insurance still exists. Earlier, some enterprises had closed down because of mutual insurance, but this process has not completely ended. There are still “zombie enterprises†caused by joint insurance and mutual reporting. Banks only supplement their working capital and reduce their expansion funds. . â— The bank surveyed reported that although most of the bad debts were processed through asset transfer, translation, and cash collection since 2017, the assets involved in the guarantee risk have not been digested. In addition, the surveyed banks are not optimistic about the prospects of traditional manufacturing. They believe that the overcapacity of traditional manufacturing industries still exists. The leading companies that have remained in the process of bankruptcy are currently in good cash flow, but due to careful consideration, enterprises generally do not Instead of lending, you choose to repay the loan or expand your reproduction by deploying your own funds. â— State-owned banks have pressure on loans, but there is no money lending, and commercial banks are more common in terms of money lending and pressure lending. Some of the companies interviewed reported that when there are certain fluctuations in the business, commercial banks will take loans and pressure loans, so the company strives to repay the commercial bank loans first. State-owned banks are better, generally do not lend money, while supplementing corporate liquidity, while compressing the expansion of new demand. â— The problem of financing is still widespread in private manufacturing enterprises, but there are big differences between enterprises and industries. Since the second half of 2016, China's financial industry “de-leverage†has been superimposed on the impact of US interest rate hikes. Although the benchmark interest rates for deposits and loans have not been adjusted due to the downward pressure on the economy, under the regulatory storm, interest rates in the money market have continued to rise, and the cost of bank debt has increased. Loan interest rates generally rose. According to our research, bank loan interest rates generally fluctuate between 20% and 30%, but the ratio of different companies and projects is quite different. For example, the interest rate of a high-tech industry loan we visited is 18% higher (good) Enterprises are up 10-20%, while another traditional leather business lending rate is about 30%. In addition, a number of good companies have indicated that their loan interest rates have not risen in the past few quarters, but have declined. â— Although the credit line has not changed, the collateral has shrunk and the loanable funds have decreased. Enterprises and banks generally report that manufacturing companies must have collateral if they want to borrow. In a traditional manufacturing enterprise, the bank credit is not compressed, but it will increase the collateral. In the past few years, the same amount of inventory discount was 50%-70% as the mortgage, and the latest discount was only 10%. â— Some respondents indicated that although the manufacturing industry is more supported in the country's large macro-level, but at the grassroots level, banks still prefer mortgages and funds flow to real estate. Banks mainly focus on profits and risks, but the risks of traditional manufacturing are still not small. The risk of investing in real estate is relatively low, and banks are more willing to invest in industries with stronger government guarantees. This situation has not changed significantly. Overall, the demand for manufacturing funds has not improved significantly, and financing conditions have not yet seen significant improvement. It is understood that in 2017, 50% of the city's new loans are personal housing loans, about 30% are infrastructure, 20% are others, and manufacturing loans are negative for 30 months, and negative growth has not yet been received. narrow. There are three reasons for the negative growth of manufacturing loans: First, good companies do not need loans because their own funds can meet the expansion of production capacity; second, the overall trend of disposing of non-performing assets and de-leverage has not changed, and we are talking about the financial cycle. During the period, the credit was tight and the direction was basically the same. Third, the demand for the manufacturing industry did not improve significantly, that is, the overall demand cake did not grow bigger, but the structural differentiation was obvious. From the bank's point of view, our research shows that most of the good companies are currently using the money brought by the profit growth to repay the loan, and the new financing demand is not much. The demand for corporate loans is mainly from new companies that attract investment in the region, but this one is not very large in general. For poorer companies, banks are more cautious and unwilling to lend. How strong is manufacturing investment? As mentioned above, there seems to be no significant improvement in manufacturing demand, so why is manufacturing investment rebounding sharply in the end of 2017? How will the future evolve? Our research results show that although the manufacturing demand is stable, the internal industry structure is gradually changing, and the manufacturing reshuffle is still in progress. The good business days are better, and the traditional enterprises are in a relatively unfavorable situation. In the process of increasing the concentration of the manufacturing industry, large manufacturing enterprises have the impulse to invest in expansion, but overall, manufacturing investment is hard to get better. The main conclusions are summarized as follows: â— First, although the overall demand for manufacturing is stable, environmental protection and safety supervision policies have led to the closure of “low-small†enterprises, orders have been transferred to large enterprises, and investment in production has increased after the increase in orders. demand. For example, the two valve companies we visited were due to the shift of orders after the closure of “Low Small†enterprises, and the demand increased, and the expansion began. The expansion will mainly start from the second half of 2017. â— Second, the environmental protection policy is becoming stricter, requiring companies to increase investment in environmentally-friendly fixed assets. For example, the leather companies we visited have increased environmental protection investment in environmental protection, and about half of their new investment is environmental protection investment. â— Third, labor costs are raised, and recruitment is difficult to exist. In order to save costs and improve enterprise efficiency, investment in fixed assets is increased through machine substitution. For example, in an enterprise that manufactures automobile motors, we have implemented machine substitutions, replacement of machinery and equipment, and increased equipment investment in fixed assets in order to save labor costs. â— Fourth, the competitive pressure, the opponents are upgrading, they will not be replaced, they will be eliminated, which also led to an increase in fixed asset investment. â— Fifth, the demand for emerging industries and government-supported industries has increased, and there is a need to expand production, but such industries account for a small proportion of manufacturing. For example, an air-energy appliance company that we visited was affected by the increase in demand for “coal to electricityâ€, and demand was skyrocketing. Enterprises are now planning to purchase land to expand production, build more plants, and expand supply. Overall, better manufacturing companies do have the need to increase investment in fixed assets, but the main reason behind this is not that demand has improved significantly. Coupled with the lack of investment momentum in the manufacturing industry and small and micro enterprises in the traditional industry, we judge that the growth rate of manufacturing investment continues to rebound significantly. It is expected that the annual manufacturing investment growth in 2018 will be around 5%, with the whole year of 2017. The difference is not too big. Indeed, public data also shows that the manufacturing investment industry is more differentiated (Figure 6).
But not all industries are plagued by cost increases, such as companies that are expanding upstream are less squeezed. The air-energy water heater companies we visited reflected that although the cost of raw materials accounted for a relatively high proportion, the company itself set up an accessory shop, and many of the parts were produced by themselves to hedge against the squeeze of profits. The good companies left in the tide of bankruptcy have stronger bargaining power and are less squeezed in the process of raw material price hikes. For example, a chemical company we visited survived after the large-scale bankruptcy caused by environmental safety supervision. Although the price of raw materials rose, the demand was stable, the demand exceeded supply, the bargaining power increased, and the prices of raw materials increased while the prices of raw materials rose. The squeeze on profits is small. There are also those companies whose pricing model is cost-plus, and the price increase of raw materials has little impact on corporate profits. For example, we are visiting a cost-added socket manufacturing enterprise with a strict budget and financial system. In advance, we will increase the price of the product according to the price of raw materials and transfer the price increase to the downstream. Auto parts companies said that raw material prices have risen, mainly by tapping and improving their ability to reduce costs and increase efficiency. The fastest-growing raw materials include plastic resins for luminaires; this squeezes profits but can reduce other costs to ease and partially pass downstream. In general, the increase in raw material prices and the increase in environmental protection costs have increased the profits of traditional manufacturing industries. However, the enterprises that have expanded upstream, the industries with bargaining power, and the cost-added industries have relatively little impact on profits. Has the financing situation improved? The regulatory storm caused the financing conditions of the whole society to tighten, the effective loan interest rate remained high, and the bond market income did not see a downward trend, while the social financing and broad money growth rates both fell sharply. So, what are the financing conditions for manufacturing? From the perspective of our research, the current bank risk appetite is still low, and the choice of lending industry is quite different. The loans are mainly invested in infrastructure, personal consumer loans and housing mortgage loans, and the development loans have not been loosened. As far as manufacturing is concerned, banks are mainly investing in emerging industries, high-tech industries and leading enterprises. The financing of traditional manufacturing and small and medium-sized enterprises is still difficult. Among the companies visited, there are two new three-board companies, one listed company, a subsidiary of a listed company (the parent company is responsible for the allocation of funds, and they will not finance at all), and the rest of the companies are financed by banks. Among the large state-owned banks interviewed, the basic situation of loan investment is as follows: â— Bank A indicates that the infrastructure accounted for 30-40% of the loans, 10% of the small and medium-sized enterprises, and the rest are personal loans. â— Bank-related loans in Bank B account for 20%, and the manufacturing industry basically does not invest in traditional industries. The main reason is that the bank previously released a large amount of loans through mortgages, joint guarantees, etc., resulting in large-scale bad, and the new lending policy is strictly Tight, does not involve traditional manufacturing, but has strong support for education, medical care, pension, tourism and other industries. â— C Bank is a supporter of township and village enterprises. It has more manufacturing loans. It is similar to Bank B. It originally invested more traditional industries, but it was later in the development zone, and the losses were less than those of Bank B. The traditional industry only supplements the working capital, does not give expansion funds, and mainly supports the development of tourism, culture, new materials, new energy, information technology and other industries. â— D-bank infrastructure loans account for 60%, personal mortgages account for 10%, and the remaining 30% are in manufacturing. Enterprises in the manufacturing industry do not enter the traditional industry, and enterprises that do not meet the environmental standards do not issue loans. The financing problems faced by the responding manufacturing enterprises are mainly reflected in the following aspects: â— The current bank loanable funds are abundant, but the overall risk appetite is still low. One important reason is that the impact of mutual insurance mutual protection still exists, and the bank The outlook for traditional manufacturing is not very optimistic, while emerging industries and leading companies have limited financing needs. Among the companies visited, the corporate debt pressure caused by joint guarantee and mutual insurance still exists. Earlier, some enterprises had closed down because of mutual insurance, but this process has not completely ended. There are still “zombie enterprises†caused by joint insurance and mutual reporting. Banks only supplement their working capital and reduce their expansion funds. . â— The bank surveyed reported that although most of the bad debts were processed through asset transfer, translation, and cash collection since 2017, the assets involved in the guarantee risk have not been digested. In addition, the surveyed banks are not optimistic about the prospects of traditional manufacturing. They believe that the overcapacity of traditional manufacturing industries still exists. The leading companies that have remained in the process of bankruptcy are currently in good cash flow, but due to careful consideration, enterprises generally do not Instead of lending, you choose to repay the loan or expand your reproduction by deploying your own funds. â— State-owned banks have pressure on loans, but there is no money lending, and commercial banks are more common in terms of money lending and pressure lending. Some of the companies interviewed reported that when there are certain fluctuations in the business, commercial banks will take loans and pressure loans, so the company strives to repay the commercial bank loans first. State-owned banks are better, generally do not lend money, while supplementing corporate liquidity, while compressing the expansion of new demand. â— The problem of financing is still widespread in private manufacturing enterprises, but there are big differences between enterprises and industries. Since the second half of 2016, China's financial industry “de-leverage†has been superimposed on the impact of US interest rate hikes. Although the benchmark interest rates for deposits and loans have not been adjusted due to the downward pressure on the economy, under the regulatory storm, interest rates in the money market have continued to rise, and the cost of bank debt has increased. Loan interest rates generally rose. According to our research, bank loan interest rates generally fluctuate between 20% and 30%, but the ratio of different companies and projects is quite different. For example, the interest rate of a high-tech industry loan we visited is 18% higher (good) Enterprises are up 10-20%, while another traditional leather business lending rate is about 30%. In addition, a number of good companies have indicated that their loan interest rates have not risen in the past few quarters, but have declined. â— Although the credit line has not changed, the collateral has shrunk and the loanable funds have decreased. Enterprises and banks generally report that manufacturing companies must have collateral if they want to borrow. In a traditional manufacturing enterprise, the bank credit is not compressed, but it will increase the collateral. In the past few years, the same amount of inventory discount was 50%-70% as the mortgage, and the latest discount was only 10%. â— Some respondents indicated that although the manufacturing industry is more supported in the country's large macro-level, but at the grassroots level, banks still prefer mortgages and funds flow to real estate. Banks mainly focus on profits and risks, but the risks of traditional manufacturing are still not small. The risk of investing in real estate is relatively low, and banks are more willing to invest in industries with stronger government guarantees. This situation has not changed significantly. Overall, the demand for manufacturing funds has not improved significantly, and financing conditions have not yet seen significant improvement. It is understood that in 2017, 50% of the city's new loans are personal housing loans, about 30% are infrastructure, 20% are others, and manufacturing loans are negative for 30 months, and negative growth has not yet been received. narrow. There are three reasons for the negative growth of manufacturing loans: First, good companies do not need loans because their own funds can meet the expansion of production capacity; second, the overall trend of disposing of non-performing assets and de-leverage has not changed, and we are talking about the financial cycle. During the period, the credit was tight and the direction was basically the same. Third, the demand for the manufacturing industry did not improve significantly, that is, the overall demand cake did not grow bigger, but the structural differentiation was obvious. From the bank's point of view, our research shows that most of the good companies are currently using the money brought by the profit growth to repay the loan, and the new financing demand is not much. The demand for corporate loans is mainly from new companies that attract investment in the region, but this one is not very large in general. For poorer companies, banks are more cautious and unwilling to lend. How strong is manufacturing investment? As mentioned above, there seems to be no significant improvement in manufacturing demand, so why is manufacturing investment rebounding sharply in the end of 2017? How will the future evolve? Our research results show that although the manufacturing demand is stable, the internal industry structure is gradually changing, and the manufacturing reshuffle is still in progress. The good business days are better, and the traditional enterprises are in a relatively unfavorable situation. In the process of increasing the concentration of the manufacturing industry, large manufacturing enterprises have the impulse to invest in expansion, but overall, manufacturing investment is hard to get better. The main conclusions are summarized as follows: â— First, although the overall demand for manufacturing is stable, environmental protection and safety supervision policies have led to the closure of “low-small†enterprises, orders have been transferred to large enterprises, and investment in production has increased after the increase in orders. demand. For example, the two valve companies we visited were due to the shift of orders after the closure of “Low Small†enterprises, and the demand increased, and the expansion began. The expansion will mainly start from the second half of 2017. â— Second, the environmental protection policy is becoming stricter, requiring companies to increase investment in environmentally-friendly fixed assets. For example, the leather companies we visited have increased environmental protection investment in environmental protection, and about half of their new investment is environmental protection investment. â— Third, labor costs are raised, and recruitment is difficult to exist. In order to save costs and improve enterprise efficiency, investment in fixed assets is increased through machine substitution. For example, in an enterprise that manufactures automobile motors, we have implemented machine substitutions, replacement of machinery and equipment, and increased equipment investment in fixed assets in order to save labor costs. â— Fourth, the competitive pressure, the opponents are upgrading, they will not be replaced, they will be eliminated, which also led to an increase in fixed asset investment. â— Fifth, the demand for emerging industries and government-supported industries has increased, and there is a need to expand production, but such industries account for a small proportion of manufacturing. For example, an air-energy appliance company that we visited was affected by the increase in demand for “coal to electricityâ€, and demand was skyrocketing. Enterprises are now planning to purchase land to expand production, build more plants, and expand supply. Overall, better manufacturing companies do have the need to increase investment in fixed assets, but the main reason behind this is not that demand has improved significantly. Coupled with the lack of investment momentum in the manufacturing industry and small and micro enterprises in the traditional industry, we judge that the growth rate of manufacturing investment continues to rebound significantly. It is expected that the annual manufacturing investment growth in 2018 will be around 5%, with the whole year of 2017. The difference is not too big. Indeed, public data also shows that the manufacturing investment industry is more differentiated (Figure 6). 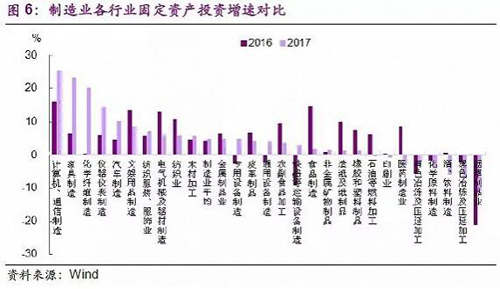 â— Under the influence of supply-side reforms, the growth rate of traditional overcapacity industry investment continues to decline, such as non-ferrous, ferrous metal smelting and rolling industries. The polluting industries are affected by environmental protection policies, and their investment growth rate continues to decline or is at a low level, such as papermaking, non-metallic mineral products, printing and dyeing, and chemical raw materials products. In addition, the growth rate of traditional manufacturing investment, which is not strong and has low added value, has continued to decline, such as leather products, food manufacturing, agricultural and sideline food processing, and cultural and recreational products. â— Investment in industries with relatively stable demand has maintained steady growth, such as automobile manufacturing and metal products. â— Increased investment in industries with more demanding industries, such as textiles and clothing (increased exports), chemical fiber (increased demand for textiles and clothing), furniture manufacturing and wood processing (affected by property lag effects). Investment in high-tech industries continues to increase, such as computer and communications equipment manufacturing, instrumentation and manufacturing. Industries with high investment growth rate in the manufacturing industry and high proportion in the whole industry, such as computer and communication manufacturing, automobiles, general equipment, electrical machinery, textiles, metal products, etc., will become the focus of the market ( Figure 7).
â— Under the influence of supply-side reforms, the growth rate of traditional overcapacity industry investment continues to decline, such as non-ferrous, ferrous metal smelting and rolling industries. The polluting industries are affected by environmental protection policies, and their investment growth rate continues to decline or is at a low level, such as papermaking, non-metallic mineral products, printing and dyeing, and chemical raw materials products. In addition, the growth rate of traditional manufacturing investment, which is not strong and has low added value, has continued to decline, such as leather products, food manufacturing, agricultural and sideline food processing, and cultural and recreational products. â— Investment in industries with relatively stable demand has maintained steady growth, such as automobile manufacturing and metal products. â— Increased investment in industries with more demanding industries, such as textiles and clothing (increased exports), chemical fiber (increased demand for textiles and clothing), furniture manufacturing and wood processing (affected by property lag effects). Investment in high-tech industries continues to increase, such as computer and communications equipment manufacturing, instrumentation and manufacturing. Industries with high investment growth rate in the manufacturing industry and high proportion in the whole industry, such as computer and communication manufacturing, automobiles, general equipment, electrical machinery, textiles, metal products, etc., will become the focus of the market ( Figure 7). 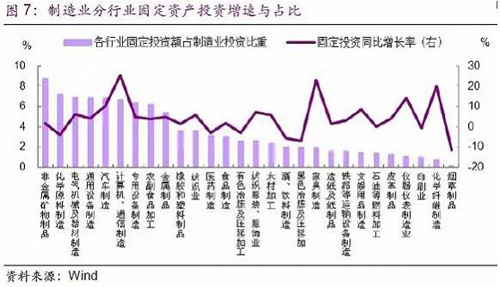 The data also shows the uneven distribution of manufacturing investment in the region (Figure 8). In 2017, fixed-income investment in Hainan, Beijing, Fujian, Yunnan, Guizhou and other regions grew at a faster rate, both exceeding 10%, mainly due to the high-tech industry development plans in various regions to drive manufacturing investment; In high-tech industries and new-type manufacturing industries, traditional industrial regions such as Northeast China and Gansu, Ningxia, have seen a sharp decline in manufacturing investment in 5%-60% in 2017; most other central and eastern provinces show a low-to-medium position of 3%-7%. Investment growth.
The data also shows the uneven distribution of manufacturing investment in the region (Figure 8). In 2017, fixed-income investment in Hainan, Beijing, Fujian, Yunnan, Guizhou and other regions grew at a faster rate, both exceeding 10%, mainly due to the high-tech industry development plans in various regions to drive manufacturing investment; In high-tech industries and new-type manufacturing industries, traditional industrial regions such as Northeast China and Gansu, Ningxia, have seen a sharp decline in manufacturing investment in 5%-60% in 2017; most other central and eastern provinces show a low-to-medium position of 3%-7%. Investment growth. 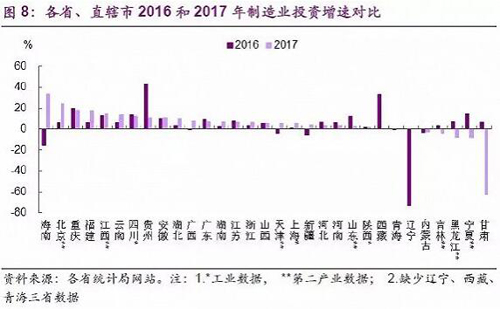 Comparing the 2016 data, it can be seen that the growth rate of investment in more than half of the provinces in 2017 increased. Among them, Hainan, Fujian, Yunnan, Guangxi and other places have seen significant growth, showing an increase of about 10%; investment growth in Hubei, Hunan, Zhejiang, Shanghai and other places rebounded slightly to 6%-10% on the basis of 2016; Chongqing, The growth rate of investment in Anhui, Guangdong, Jiangsu, Shanxi, Shaanxi and other places was basically the same as that in 2016; in the northeastern provinces such as Northeast China and Ningxia in Gansu, the growth rate of manufacturing investment in 2017 was positively negative and investment declined. The rebound in the data on manufacturing investment in 2017 has a certain relationship with the supply-side reform and environmental protection “low-small†enterprises. After the “low-small†enterprises closed down, orders were transferred to large enterprises, which led to the expansion of large enterprises. The original fixed asset investment of “Low Small†enterprises is not included in the statistics, and the expansion of large enterprises is included in the statistics. This may be an important reason for the rebound in manufacturing investment in 2017. (Source: Wenhua Macro Text / Everbright Securities analyst Zhang Wenlang Guo Yongbin Huang Wenjing)
Comparing the 2016 data, it can be seen that the growth rate of investment in more than half of the provinces in 2017 increased. Among them, Hainan, Fujian, Yunnan, Guangxi and other places have seen significant growth, showing an increase of about 10%; investment growth in Hubei, Hunan, Zhejiang, Shanghai and other places rebounded slightly to 6%-10% on the basis of 2016; Chongqing, The growth rate of investment in Anhui, Guangdong, Jiangsu, Shanxi, Shaanxi and other places was basically the same as that in 2016; in the northeastern provinces such as Northeast China and Ningxia in Gansu, the growth rate of manufacturing investment in 2017 was positively negative and investment declined. The rebound in the data on manufacturing investment in 2017 has a certain relationship with the supply-side reform and environmental protection “low-small†enterprises. After the “low-small†enterprises closed down, orders were transferred to large enterprises, which led to the expansion of large enterprises. The original fixed asset investment of “Low Small†enterprises is not included in the statistics, and the expansion of large enterprises is included in the statistics. This may be an important reason for the rebound in manufacturing investment in 2017. (Source: Wenhua Macro Text / Everbright Securities analyst Zhang Wenlang Guo Yongbin Huang Wenjing)
The recent evolution of manufacturing investment is puzzling. The growth rate of fixed asset investment in the manufacturing industry declined all the way in the past few years, and it steadily warmed up in the middle of 2016. However, it gradually fell back after the second quarter of last year. Unexpectedly, the decline in the previous period was changed in December, and the Jedi rebounded. In the first 11 months of 2017, the growth rate of fixed asset investment in manufacturing industry was only 4.1%, but it increased by 4.8% for the whole year (up from 4.2% in 2016), which is the sharp increase in the last month (Figure 1). The rebound has become the main contributor to the rebound in manufacturing investment. Under this circumstance, the market has no prospects for the manufacturing industry. Some people think that China's manufacturing industry has already blossomed, and this year's manufacturing investment will rebound strongly. So what is the manufacturing industry? Is the investment rebound a short-lived or a reversal?