This article makes a simple comparison of the two types of high-strength bolts to help you understand the difference. The core point is to understand the two concepts of "torque coefficient" and "tightening axial force". 01. High-strength bolt large hexagonal and torsional shear type High-strength bolts are easily distinguished from the outer shape by a Hex head, which is abbreviated as HSFG (High strength friction grid bolts). As the name suggests, the nut of a large hex head bolt is a regular hexagon, which can be inferred to be convenient for the use of a wrench (described in more detail later), which is the type of high-strength bolt originally used. Troque shear style / Twist off bolts /, commonly referred to as TCB (Tension control bolts) in English to distinguish. The end of the end has a spline-end, and the nut of the bolt is generally circular (no need to use a wrench); it is an improved product developed by the Japanese on the basis of HSFG. Hexagon head bolts are constructed with a fixed torque wrench. Because they do not hold the screw when they are screwed, the screw may be driven to “co-rotate†while rotating the nut. The torque value is not used, and the screw cannot be tightened. Therefore, the screw head is designed as a large hexagon, and in the case of the same rotation, it can be temporarily fixed by an ordinary wrench to avoid the phenomenon of the same rotation. The support rod extended by the torque wrench is mainly used to provide the fulcrum to determine the torque applied, so if there is no reliable fulcrum, the wrench can not be constructed. Twisted type (1)* : (Plum head) The torsion-shear type bolt is constructed with a torsion-shear type wrench, and the root uses a forward-reverse torsion bar to directly clamp the screw itself through the "plum head", so the same rotation phenomenon does not occur when the screw is applied. The idea of ​​product design is: when the pre-tension value is reached by the screw, the material can withstand the corresponding shear force, and the root section of the plum blossom head is weakened to achieve the purpose of cutting. 2, the principle comparison analysis First of all, it must be understood that the pre-tension design values ​​of the same model of large hexagonal and torsional shear bolts can be achieved under the correct construction method. Large hexagonal high-strength bolt (HSFG) screwing process: (understand "torque coefficient") "541" principle The "541" principle is a correspondence between the torque value and the preload force that the Japanese have repeatedly experimented on based on engineering practice. This is cited and elaborated in the British Steel Structure Textbook, which gives the factors of torque loss. In the domestic steel structure education, the "541" principle is rarely mentioned, but the direct response becomes the "torque coefficient" we understand: Effective clamping force / total output torque = torque factor (0.11~0.14) (2)* Therefore, the "torque coefficient" is the most important parameter for the construction of large hexagonal high-strength bolt HSFG. In order to ensure the construction quality of large hexagon bolts, the torque coefficient must be tested and tested. Twist-cut high-strength bolt (TCB) screwing process: (understand "tightening axial force") Weakening the cutting process of the section While the tensile stress in the applied torque accumulating material reaches the design value ("tightening axial force"), the corresponding shear strength of the material just causes the plum blossom head to weaken the cross-section. Therefore, in order to ensure the construction quality of the torsion-shear type bolt, it is necessary to measure the "fastening axial force" corresponding to the representative of the shearing. Its value should be in accordance with the pre-tightening design value. 03. Comparison of torsional shear and large hexagon According to the national standard JGJ-82 6.1.1, in the high-strength bolt connection pair, the large hexagon bolt requires two pads and one mother, and the torsion-cut high-strength bolt requires one pad and one mother. (3)* Comparison of acceptance methods The large hexagon bolt HSFG is tested with a fixed torque wrench after construction. When accepting the torsion-shear type TCB, pay attention to the plum blossom head being broken and qualified. 03. Summary The torsion-shear type is an upgraded version of the large hexagon. The price is slightly expensive, the construction and inspection are relatively simple, and the advantages are obvious. However, due to the limitation of the national standard product model (only 10.9, the largest size is 24M). (4)* The key to understanding its core principles is to master: "torque coefficient" and "tightening axial force" two concepts. View (1)*: According to BS EN 14399, the torsion-shear type bolt can also have the form of a hex head, but according to the principle of tightening, the hex head is no longer needed. In order to save material, it is omitted in the national standard. (2)*: It can be seen that the torque coefficient value is about 10%, which is consistent with the conclusion of the “541†principle. The purpose of introducing the "541" principle here is that it relates to the understanding of what is the frictional surface that we will talk about later. (3)*: The rules in the British Standard and American Standard are different for the use of several gaskets. The national standard is the safest in all situations. It is not necessary for the construction personnel to consider the construction situation on the site, but it can be used only, and the waste is not big anyway. (4)*: In practice, some friends have feedback that the torsion-shear type bolts are less used in railway steel bridges, roller coasters, etc., which are directly subjected to vibration load structures. After careful observation, the author found that this is the case in China, but the vibration load must not be the reason for limiting the use of torsion-shear bolts. Another large hex bolt is convenient for re-threading for inspection and maintenance. Because the national standards all highly emphasize the one-off of the high-strength bolts, that is, they will fail after the relaxation, and the bolts need to be replaced. The double twist is not allowed. Because the size specifications of TCB bolts in the Anglo-American standard are far greater than the national standard, for example, Abu Dhabi uses the M36 produced by the British TCB bolt factory, and the torsional shear type TCB bolt (unit price is more than 100 yuan), it is used in the project to withstand vibration. The core position of the load. And GB/T 3632 1.1 directly indicates that the torsional shear type high-strength bolt is suitable for railway steel bridges. Rutile Tio2,Titanium Pigment,Titanium White Paint,Titanium Dioxide In Makeup TINOX CHEMIE GMBH , https://www.tinoxglobal.com
1. Comparative analysis of appearance 
Large hexagon: 



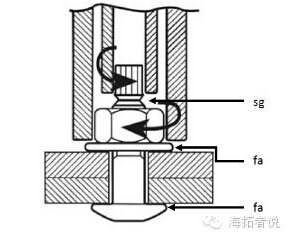
The analysis shows that even the torsion-shear type bolt does not directly feed back the pre-tension value in the screw, but replaces it with the shearing ability. The test item is still not a direct item, and there is a substitution error. 
Connection vice composition comparison 
Therefore, the author believes that the current standard-made torsion-shear type bolt type is limited (only 10.9, the maximum diameter is only M24), which is the root cause of limiting the use of torsional shear bolts in railway steel bridges and other structures. Combined with the poor performance of our domestic "bolt gun", it can be seen that as a manufacturing country, we have obvious differences in the preparation of detailed products and international advanced.