Cosmetics is a variety of raw materials through a reasonable deployment of processing from the compound mixture. Cosmetics with a wide range of raw materials, different performance. According to the Raw Material properties and uses of cosmetics, can be divided into matrix materials and auxiliary raw materials in two categories. The former is a class of cosmetics in the main raw materials, cosmetics in the possession of a large proportion of the cosmetics play a major role in the role of the material. The latter is the formation of cosmetics, stability or to give color, smell and other characteristics of the role of these substances in the cosmetic formula is not used, but it is extremely important. Cosmetics are natural, synthetic or extracted from the role of different substances as raw materials, by heating, mixing and emulsification and other production processes processed from the chemical mixture.
Cosmetic Raw Materials Cosmetic Raw Materials,Hyaluronic Acid Cosmetic Grade,Arbutin Cosmetic Raw Material,Isosorbide Dimethyl Ether SHANDONG ZHISHANG CHEMICAL CO.LTD , https://www.zhishangchemical.com
The higher the performance of electronic products, the more difficult thermal management, because as the power density of semiconductor components continues to increase, the heat flux will become larger and larger, some even up to tens of kilowatts per square centimeter, which is five times the surface of the sun.
If such large heat is not able to be diverged from the components in time, it will seriously threaten the stability of electronic products. Some studies [1] have shown that more than half of the faults in electronic devices are caused by heat-related problems. For example, our most common smart phones, although a large number of graphite thermal conductive sheets and aerospace alloy materials have been used, but they have seen a certain machine in two days, because the "world's strongest mobile phone processor" caused overheating and burned the motherboard. News... All this tells us:
With the demand for thinner and more efficient terminal products, the development direction of semiconductor solutions has not only improved performance, but also the heat generation and heat dissipation performance have become quite important factors in semiconductor design. The heat generation is mainly related to the chip manufacturing process and the temperature control algorithm, while the heat dissipation performance can work on the material and product structure.
Here we will introduce the use of chemical vapor deposition (CVD) diamond as a new advanced thermal management solution, especially for RF power amplifiers. CVD diamond heat sinks have been proven to reduce overall package thermal resistance, which far exceeds other commonly used materials.
Where is CVD diamond better than traditional heat sinking materials?
As an immediate family member of diamonds, diamonds with "carbon elemental" properties are not small, including the highest known thermal conductivity, stiffness and hardness, while having high optical transmission characteristics, low expansion coefficient and low density over a large wavelength range. Attributes. These properties make diamond a thermal management application that significantly reduces thermal resistance.
To synthesize the diamonds needed for thermal management applications, the first step is to choose the most appropriate deposition technique. Microwave-assisted CVD provides better control of grain size and grain boundaries to produce high-quality, highly reproducible polycrystalline diamonds that meet the specific application thermal conductivity levels. At present, CVD diamond has been commercialized and has different grades of thermal conductivity of 1000-2000 W/mK. CVD diamonds also have fully isotropic features that enhance heat dissipation in all directions. Figure 1 shows the thermal conductivity of CVD diamond versus other conventional heat sink materials. 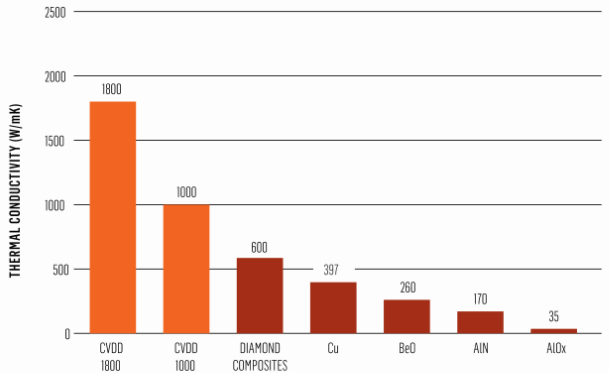
Figure: Thermal conductivity comparison between CVD diamond and "traditional" thermal materials
With recent technological developments, CVD diamonds have been mass-produced and costs have fallen rapidly. The mass production cost of CVD diamond heat sinks without metallization is $1/mass, and the price is mainly determined by the thermal conductivity rating. For applications where the common thickness and lateral dimension between 0.25-0.40mm is equal to the wafer size, the RF device diamond heat sink size is typically less than 5 cubic millimeters. As a result, an additional incremental cost of a few dollars at the chip level can significantly reduce system cost. For example, if the system can be operated at higher temperatures, the initial cost of the cooling subsystem and subsequent ongoing operating costs can be reduced. With the appropriate die attach method, the diamond heatsink provides a reliable thermal management solution for semiconductor packages.
Abstract I don't know when, more and more electronic products began to advertise themselves as "fever." At the beginning, "fever" was to highlight the high performance of the product, but later, it became a consumer tune product...
I don't know when, more and more electronic products began to advertise themselves as "fever." In the beginning, "fever" was intended to highlight the high performance of the product, but later it became a derogatory term for consumers to over-temperature the product.